Chemical Reactions - The fact that atoms are conserved, together with knowledge of the chemical properties of the elements involved, can be used to describe and predict chemical reactions.
Chemical Reactions - The fact that atoms are conserved, together with knowledge of the chemical properties of the elements involved, can be used to describe and predict chemical reactions.: Overview
This topic covers various concepts like Terms in Second Law of Thermodynamics, , etc.
Important Questions on Chemical Reactions - The fact that atoms are conserved, together with knowledge of the chemical properties of the elements involved, can be used to describe and predict chemical reactions.
From the data of following bond energies:
Calculate the enthalpy of the following reaction in .
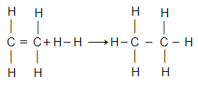
Given that bond energies of respectively and for , bond enthalpy of is:
Consider the following reactions
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
Enthalpy of formation of
The enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is If resonance energy of benzene is its enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene would be
For which one of the following equations is equal to for the product?
What is the enthalpy change for,
if heat of formation of are and respectively (in standard conditions)?
Enthalpy of is negative. If enthalpy of combustion of and are x and y respectively, then which relation is correct:
The values of heat of formation of are –298.2 kJ and –98.2 kJ. The enthalpy change of the reaction
will be
Consider the following reaction occurring in automobile
the sign of would be:
Bond dissociation enthalpy of respectively. The enthalpy of formation of HCl is:
A chemical reaction will be spontaneous if it is accompanied by a decrease of
Assume each reaction is carried out in an open container. For which reaction will
The enthalpy and entropy change for the reaction
are respectively. The temperature at which the reaction will be in equilibrium is
The absolute enthalpy of neutralisation of the reaction:
will be:
[Consider the actual value instead of magnitude].
For the reaction:
at constant temperature, is:
What is the entropy change (in ) when one mole of ice is converted into water at ? (The enthalpy change for the conversion of ice to liquid water )
of an ideal gas at temperature is expanded reversibly from to . Find the entropy change.
The entropy change in the fusion of one mole of a solid melting at (Latent heat of fusion, ) is:
The Nernst equation for the reaction, , in terms of the free energy change is:
Enthalpy of neutralisation of acetic acid by is . Calculate for ionisation of . Given the heat of neutralisation of a strong acid with a strong base is .
